Cyber Security Dilemmas: Data Leaks
The pre-Christmas rush is in full swing. In search of gifts for their loved ones, people are increasingly willing to “storm” online shops
 GO BACK
GO BACK
Remix is a full-stack web framework focused on web fundamentals and modern UX.
Yes this is yet another JS framework but just stick for a bit longer as this framework is made by Michael Jackson and Ryan Florence the smart guys behind React Router. Hope that got your attention, so let’s see what’s good about the Remix framework.
Remix is a server side framework built on top of the Web Fetch API and React Router, each route in remix have three primary exports a loader, an action and a default component export. The loader function will be called on the server before rendering to provide data to the route, the action function is responsible for data mutation, the default export is the component that will be rendered on that route. The loader and action functions are run server side only and must return a Response object, the default export is run both on server and client side.
To initialize a new Remix project:
npx create-remix@latest
IMPORTANT: Choose "Just the basics", and then "Remix App Server" when prompted
cd [whatever you named the project]
npm run dev
```Open up http://localhost:3000. the create-remix command will get you a starter template with the following structure:
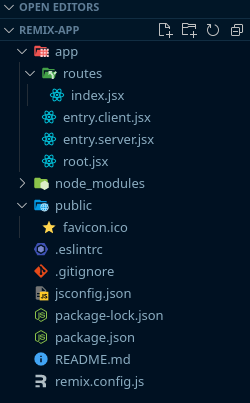
app folder will contain all your application routes and code.app/entry.client.jsx is the first piece of code that runs in the browser and is used to hydrate the React components.app/entry.server.jsx is the first piece of code that runs when a request hits the server, this file renders our React app to a string/stream and send that as our response to the client.app/root.jsx is where the root component goes.app/routes/ is where all your route modules will go, remix uses a file-system based routing.public folder is where your static assets go (images/fonts/etc).remix.config.js is where the remix configuration can be set.Let’s check a login.jsx route example inside of a Remix app:
import { redirect, json, Form, useActionData, useTransition } from 'remix';
import { isLoggedIn, verifyLogin } from '../auth';
export const loader = async ({ request }) => {
if (await isLoggedIn(request)) {
return redirect('/dashboard');
}
return json({ success: true });
};
export const action = async ({ request }) => {
const formData = await request.formData();
const values = {
email: formData.get('email') ?? '',
password: formData.get('password') ?? '',
};
const errors = await verifyLogin(values);
if (errors) {
return json({ errors }, { status: 400 });
}
return redirect('/dashboard');
};
export default function LoginRoute() {
const actionData = useActionData();
const transition = useTransition();
const isSubmitting = transition.state === 'submitting';
return (
Email
{actionData?.errors?.email &&
{actionData.errors.email}
}
<div>
<label htmlFor="password">Password</label>
<input id="password" name="password" type="password" />
{actionData?.errors?.password && (
<div>{actionData.errors.password}</div>
)}
</div>
<div>
<button type="submit" disabled={isSubmitting}>
{`Login ${isSubmitting ? '...' : ''}`}
</button>
</div>
</Form>
);
}
```The first thing happening here is the loader function checking if the user is already logged in with the isLoggedIn function and will redirect him to the /dashboard route, if not it will simply return a { success: true } response, then the login page gets rendered.
The LoginRoute renders a form with an email and password inputs and a submit button, as you can see there are no state variables nor an onSubmit event handler in our component, it is because in remix every route can export an action and when a form is submitted with a POST method the action will be called and will handle that event.
When the form gets submitted the action function will get the
FormData from the Request object const formData = await request.formData(), then are we are constructing the values object with an email and password properties, the formData.get('email') will look for the first matching field inside our form with a name="email" property and return its value. We are checking if the credentials are correct with the verifyLogin function, here you could use any of your favorite JS schema validation library and do a fetch to your custom backend to check if the login data are correct, if so we redirect the user to the /dashboard route, else we return a json response with the errors object and an HTTP status code 400, the useActionData hook will return this errors object if there is any and we conditionnaly render the error message as in {actionData?.errors?.email && <div>{actionData.errors.email}</div>}.
The useTransition hook tells us everything about the page transition state, with the isSubmitting variable we are checking when a submission is occurring, if there is any we will disable the submit button and show Login.... instead of Login, we could also show to the user a loading spinner or any other indication instead.
The json function is just a shortcut for creating application/json response objects. The useLoaderData hook returns the JSON parsed data from your route loader, the useActionData returns the route action parsed data.
Each route can also export a meta function responsible for setting meta tags for your Html document, this way you can set a title and a description for every route and add any Open Graph or other meta tags you want.
export const meta = () => {
const title = 'My Awesome Page';
const description = 'Super awesome page';
return {
charset: 'utf-8',
title,
description,
keywords: 'Remix,Awesome',
'twitter:image': 'https://awesome-page.com/awesome.png',
'twitter:card': 'summarylargeimage',
'twitter:creator': '@awesome',
'twitter:site': '@awesome',
'twitter:title': title,
'twitter:description': description,
};
};
export default function AwesomeRoute() {
return
Awesome Route
;
}
```We have just tackled the tip of the iceberg about Remix, there is so much more to know, here are some useful links:
What’s great about Remix is by getting better with it you’ll get better at web fundamentals, as you have seen many of this article links point to the Mozilla docs, this is what is meant by Remix being focused on web fundamentals it uses Web APIs like the Response and Request object to provide the users with a great UX plus you can still use all your React usual techniques and favorite libraries.
We didn’t talk about all the great features provided by Remix in this article like Nested Routes, Error Boundaries, Remix Stacks but still, this article should give you a good idea about the philosophy behind Remix.
